You probably wonder if paper vs plastic bags really makes a difference for the planet. The answer is not as simple as you might think. For each paper bag, factories emit about 5.5 kg of CO2, which is over three times more than a plastic bag. Paper bags also use much more energy to produce. Yet, plastic bags stick around in nature for years and cause pollution. You want to know which one is better for the environment, right? Let’s break it down with real numbers and facts.
Key Takeaways
- Consider the entire life cycle of bags. Look at how they are made, used, and disposed of to understand their true environmental impact.
- Paper bags break down faster and are easier to recycle, but they require more energy and water to produce than plastic bags.
- Plastic bags use fewer resources to make but can pollute the environment for hundreds of years and harm wildlife.
- Reusing bags is key. The more you use a bag, the better it is for the planet. Aim to use reusable bags many times to reduce waste.
- Make eco-friendly choices when shopping. Bring your own bags, skip bags for small purchases, and recycle or compost used bags.
Environmental Impact: Paper vs Plastic Bags

Life Cycle Analysis
To find out which bag is better for the planet, you need to look at the whole process. Life cycle analysis helps with this. It checks every step in a bag’s life. This includes getting materials, making the bag, using it, and throwing it away.
Here are the main steps in a bag’s life:
- Raw material extraction
- Manufacturing processes
- Usage
- End-of-life disposal
If you skip a step, you do not see the full impact. For example, if you only look at how much energy it takes to make a bag, you might think plastic is always better. But if you look at what happens after you use the bag, things change. Paper bags break down in nature. Plastic bags can stay in the environment for hundreds of years.
You can see some important facts from life cycle analysis in this table:
| Key Findings | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Paper bags usually do better with recycling and littering than plastic bags. |
| Production Resources | Paper bags need more energy and water to make than plastic bags. |
| Littering Consideration | Paper bags have a clear advantage when you look at littering. |
Key Factors Compared
You might wonder what really matters when you compare paper and plastic bags. Here are the most important things to think about:
- Greenhouse gas emissions
- Water use
- Pollution
- Waste generation
- Biodegradability
- Impact on wildlife
This table shows how paper and plastic bags compare in these areas:
| Comparison | Paper Bags | Plastic Bags |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Required | Higher | Lower |
| Water Usage | Higher | Lower |
| Recycling Potential | Higher | Lower |
Now, let’s look at some numbers. This chart shows how each bag type affects the environment in different ways:
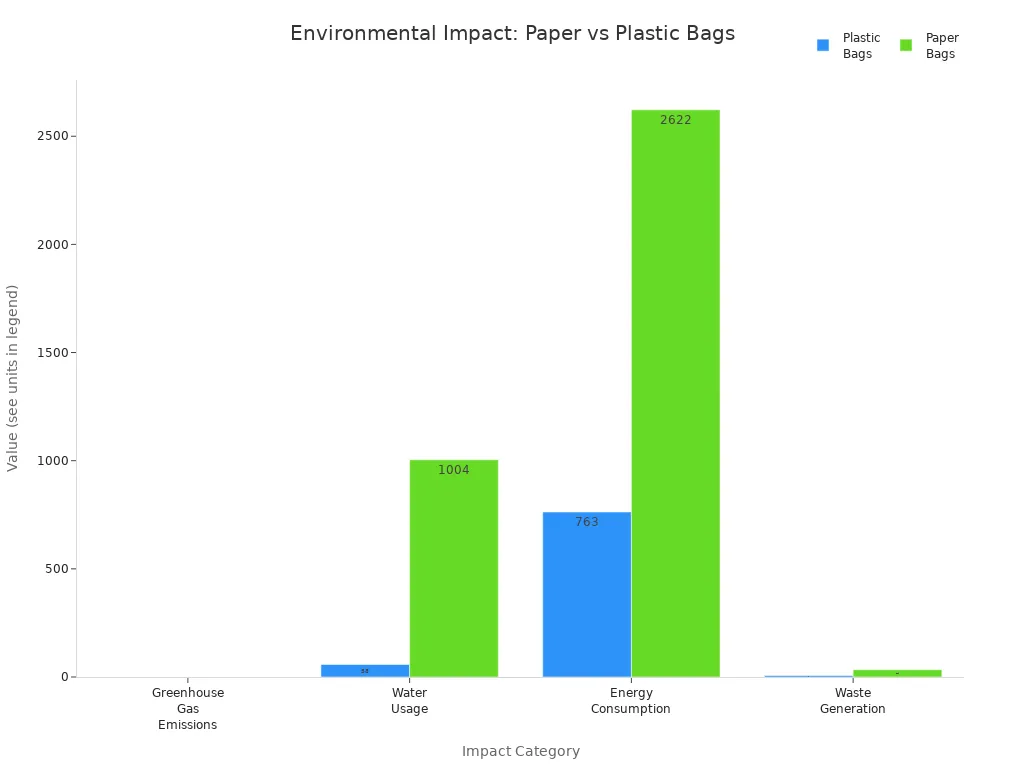
You can also see the details in this table:
| Category | Plastic Bags | Paper Bags |
|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | 0.04 tons of CO2 | 0.08 tons of CO2 |
| Water Usage | 58 gallons | 1,004 gallons |
| Energy Consumption | 763 megajoules | 2,622 megajoules |
| Waste Generation | 7 kg of waste | 33.9 kg of waste |
Tip: Even though paper bags use more water and energy, they break down faster and are easier to recycle. Plastic bags use less energy and water, but they can cause more long-term pollution.
Let’s compare some other important things:
| Environmental Factor | Paper Bags | Plastic Bags |
|---|---|---|
| Production Materials | Made from trees, a renewable resource | Made from fossil fuels, a non-renewable resource |
| Biodegradability | Naturally decompose without polluting | Do not biodegrade, break into microplastics |
| Carbon Footprint | Require more energy to produce, lower long-term burden | Require less energy, cause long-term pollution |
| Recycling Capabilities | Widely accepted for recycling, compostable | Difficult to recycle, often not accepted |
| Impact on Wildlife | Break down naturally, less risk to animals | Frequently mistaken for food, harm wildlife |
Both types of bags have good and bad points. Paper bags have a bigger impact when they are made, but they are easier to recycle and do not last as litter. Plastic bags use fewer resources to make, but they can pollute the environment for a long time and hurt animals.
So, when you pick a bag, think about the whole impact. Look at how it is made, how you use it, and what happens when you throw it away. This helps you make a better choice for the planet.
Paper Bags: Production and Impact
Resource Use and Emissions
Choosing paper bags may seem good for nature. But making paper bags uses many resources. Factories cut down trees to make them. Fewer trees means less clean air. Making paper bags needs lots of energy. It takes about four times more energy than plastic bags. Most energy comes from burning fossil fuels. This adds greenhouse gases to the air.
Here’s a simple look at water and energy use for each bag:
| Bag Type | Water Requirement (gallons) | Energy Requirement (barrels of oil) |
|---|---|---|
| Paper Bags | At least 1 | 15,100 |
| Plastic Bags | Less than 0.05 | 8,300 |
Making paper bags causes more pollution. They create more dirty air and water than plastic bags. Making paper bags makes 70% more air pollution. It also makes 50% more water pollution. Paper bags are heavier than plastic bags. Trucks need more fuel to move them. This means more emissions.
Pollution and Waste
You may not know how much pollution comes from paper bags. Factories that make paper bags pollute the air and water. Here are some facts:
- Paper bags make 70 times more air pollution than plastic bags.
- They make 50 times more water pollution.
- Making one paper bag uses four times more water than a plastic bag.
This pollution can hurt rivers and lakes. It can also harm the air you breathe. Paper bags take up more space in landfills. They are bulkier than plastic bags.
Biodegradability and Disposal
Unlike plastic bags, which can stay in nature for centuries, paper carry bags break down naturally if thrown away the right way.
Paper bags break down and can be recycled. This makes them better for the planet than plastic bags. But if you throw them away after one use, they can still cause problems. If paper bags go to landfills, they can add to litter. They also make greenhouse gases as they break down.
You can compost paper bags. They will break down over time. If you put them in the trash, they may end up in a landfill. There, they break down slowly and can pollute. Using paper bags again or recycling them helps the planet.
Plastic Bags: Production and Impact
Resource Use and Emissions
When you look at plastic bags, you might think they are easy to make. The truth is, the process uses different types of plastic like PET, PE, PP, and PVC. Each type needs its own amount of energy and creates different emissions. Here’s how the production of plastic bags stacks up:
- Factories use different plastics, each with its own energy needs.
- Shipping materials and finished plastic bags adds more carbon emissions. Trucks and ships burn fuel, and sometimes products need refrigeration.
- If you throw away plastic bags the wrong way, they can end up in landfills. There, they release methane, a strong greenhouse gas.
Plastic bags use less energy to make than paper bags. Paper bags need about four times more energy because turning wood into paper is a tough job. So, plastic bags win in energy use, but there’s more to the story.
Pollution and Waste
Plastic bags create many types of pollution. You see them blowing around in streets, parks, and rivers. During production, resin pellets can leak out and pollute the environment. When people don’t manage waste well, plastic bags end up as litter. Over time, they break down into microplastics. These tiny pieces get into soil, water, and even the food you eat.
- Resin pellets escape during production.
- Littering spreads plastic bags everywhere.
- Microplastics come from wear and tear.
- Urban runoff washes plastic bags into rivers and oceans.
- Washing machines send microplastics into wastewater.
- Marine animals get tangled in plastic bags.
- Wildlife sometimes eats plastic bags, thinking they are food.
- Trees and plants can’t grow well when plastic bags wrap around their roots.
Every year, people use up to one trillion plastic bags worldwide. About 10% of these end up in the ocean. That means 66 billion plastic bags float in the sea each year. Plastic bags make up 5% of global plastic waste, which equals 550,000 tons entering the ocean.
Persistence and Disposal
Plastic bags stick around for a long time. If you toss them in the trash, most will not get recycled. Less than 1% of plastic waste gets recycled because machines can’t handle plastic bags well. Most single-use plastic bags last for hundreds of years in nature.
| Environmental Consequence | Description |
|---|---|
| Harm to Wildlife | Plastic bags hurt animals on land and in the ocean. Microplastics enter food chains. |
| Pollution of Waterways | Plastic bags add microplastics to soil, rivers, and habitats. |
| Long-term Degradation | Plastic bags take 20-500 years to break down, releasing toxic chemicals. |
You see plastic bags everywhere, from city streets to beaches. They do not break down like paper bags. Instead, they stay in the environment, causing problems for people, animals, and plants.
Head-to-Head Comparison: Paper vs Plastic Bags
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
It might seem simple to pick a bag based on greenhouse gases. But it is not that easy. Using a plastic bag once makes less carbon than using a paper bag once. If you use a paper bag four times, it does better than plastic. The materials and how bags are made matter a lot.
Here’s a quick look at the carbon emissions:
| Bag Type | Carbon Emissions (Single Use) | Carbon Emissions (Multiple Uses) |
|---|---|---|
| Plastic Bag | Lowest | Higher than reused paper bags |
| Paper Bag | Higher | Lower if reused four times |
| Reusable Bag | N/A | Lower if used at least eleven times |
- Plastic bags have the lowest carbon if used once.
- Paper bags do better if you use them many times.
- How you use bags changes their effect on the planet.
To lower your carbon footprint, reuse your bags. Every time you reuse a bag, you help the Earth.
Water and Air Pollution
You need to think about water and air pollution too. Making paper bags causes 70% more air pollution than plastic bags. It also makes 50 times more water pollution. Paper bag factories use four times more water and 10% more energy than plastic bag factories.
| Type of Bag | Air Pollution Increase | Water Pollution Increase | Energy Consumption | Water Consumption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper | 70% more | 50 times more | 10% more | 4 times more |
| Plastic | Baseline | Baseline | Baseline | Baseline |
A study in Scotland found that paper bags can cause algae to grow in lakes and rivers. This happens because paper factories put too many nutrients in the water. The extra nutrients use up the oxygen. Fish and other animals can die from this.
- Paper bags make more air pollution and greenhouse gases.
- Plastic bags have less effect on water and air when made.
- Paper factories can hurt water quality and cause algae blooms.
If you care about clean water and air, think about how your bag was made.
Waste Generation
Waste is a big problem for both types of bags. In cities, schools put plastic waste in dustbins. In rural areas, people often burn plastic bags outside. This makes harmful smoke. Paper waste is also burned in rural places. In cities, paper waste goes in dustbins.
- City schools keep plastic waste in dustbins.
- Rural schools burn plastic bags outside.
- Paper waste goes in dustbins in cities, but is burned in rural areas.
Burning plastic bags makes toxic smoke. Burning paper bags is less harmful, but still pollutes. If you throw bags in the trash, they go to landfills. Paper bags take up more space because they are bigger. Plastic bags are lighter, but last much longer.
You can help by reusing or recycling your bags. Try not to burn them or throw them in open piles.
Biodegradability
Paper bags break down much faster than plastic bags. Paper bags can decompose in weeks or months. Plastic bags can last for hundreds of years. Warm, wet places with lots of microbes help paper bags break down. Plastic bags do not break down easily anywhere.
| Feature | Paper Bags | Plastic Bags |
|---|---|---|
| Biodegradability | Decomposes in weeks to months | Persists for hundreds of years |
| Environmental Conditions | Influenced by temperature, humidity, and microorganisms | Resistant to decomposition |
| Impact on Wildlife | Lesser threat, breaks down harmlessly | Significant threat, can be ingested |
- Paper bags break down and do not hurt animals.
- Plastic bags can choke or poison animals.
- Microplastics from plastic bags get into soil, water, and food.
If you want a bag that disappears fast and does not hurt animals, pick paper bags.
Reusable Bags and Sustainable Choices

Benefits of Reusable Bags
You may ask why reusable bags are better for the planet. Using reusable bags helps cut down on pollution and waste. These bags make shopping less harmful to nature. Look at this table to see the differences:
| Type of Bag | Environmental Impact | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| Reusable Bags | Lower environmental impact when used many times, less waste builds up. | Must be reused often to balance out making them. |
| Single-Use Plastic | Adds a lot to pollution and waste. | Each use harms the environment more, causing extra trash. |
| Paper Bags | Break down in nature but need more resources to make. | Best if reused or recycled; not as good if used once. |
You need to use reusable bags many times to help the earth. For example, a cloth bag or tote should be used about 7,100 times to balance out making it. Cotton bags need hundreds of uses to be better for the planet. Every time you reuse a bag, you help nature. The more you use your bag, the more you help the environment.
- Reusable bags help lower pollution and waste.
- You need to use them many times to make a big difference.
- Using your bag more is better for the planet.
Tip: Pick reusable bags that are strong and easy to wash. Take them every time you shop to help the environment more.
How to Reduce Environmental Impact
You can make better choices every time you shop. Here are some easy ways to help the planet:
- Bring your own reusable bags to the store.
- Skip a bag if you buy only a few things.
- Use your bags again and again.
- Throw away bags the right way after using them.
- Join groups that ask people to bring their own bags.
- Shop at stores that reward you for using reusable bags.
Stores can help you make good choices too. They can give discounts or points when you use reusable bags. Stores can work with local groups to teach people about eco-friendly habits. You might see reusable bags at the front of stores to remind you to use them.
| Strategy Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Incentives | Give discounts or points for using reusable bags. |
| Community Engagement | Work with local groups to teach eco-friendly habits at events. |
| Visibility of Reusable Bags | Put reusable bags where customers can see them to encourage use. |
Note: The best choice is to use your bags as many times as you can. Every time you do, you help the planet and make the world cleaner.
Conclusion
You want to help the planet with your choice. Plastic bags need less energy to make. But they stay around for hundreds of years. They can hurt animals. Paper bags break down quickly. They are easy to recycle. They help people make eco-friendly choices. Here are some facts:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Structural Integrity | Multi-layer paper bags hold more weight than plastic. |
| Biodegradability | Paper bags break down in weeks, not years. |
| Recyclability | You can recycle paper bags. This lowers carbon emissions. |
Many stores and governments use fewer plastic bags now. People like packaging that is better for nature. If you want a cool and green bag for shopping or gifts, INITI has custom paper bags. These bags show you care about the earth.
FAQ
What makes paper bags better for the environment?
You can recycle paper bags easily. They break down in nature much faster than plastic. If you throw them away, they do not stay in landfills for hundreds of years.
Why do plastic bags cause so much pollution?
Plastic bags do not break down quickly. They can turn into tiny pieces called microplastics. Animals can eat them by mistake. You often see single-use plastic bags in rivers and parks.
Can I reuse paper bags?
Yes, you can reuse paper bags for shopping or storage. If you keep them dry, they last longer. When you finish using them, you can recycle or compost them.
How many times should I use a reusable bag?
Try to use your reusable bag as many times as you can. Using it at least 10 times helps lower its impact on the planet. The more you use it, the better.
What should I do with old bags?
You can recycle paper bags. For plastic bags, check if your store has a special bin. Never throw bags in nature. Reuse them if possible.




