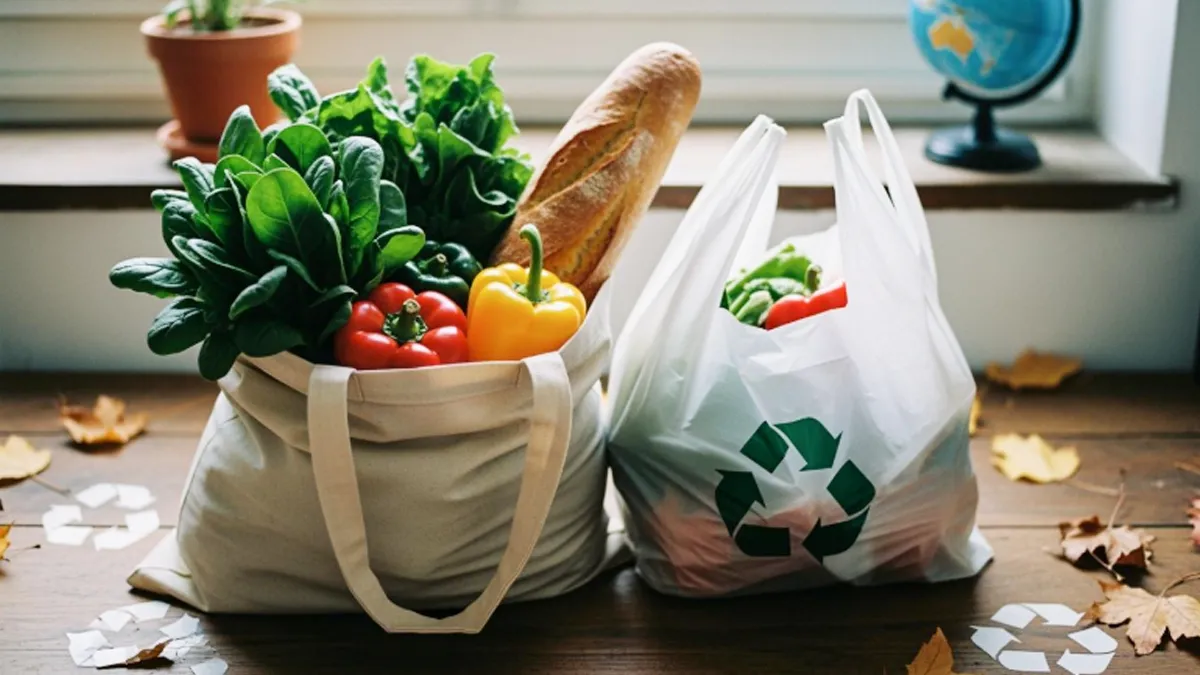
If you want to help the environment, you may wonder which bag is better. You can choose between reusable shopping bags or plastic bags. The answer depends on how many times you use each bag. You look at things like carbon emissions, water use, waste, and pollution to measure the impact.
Key Takeaways
- Plastic bags are cheap and easy to use. But they stay in landfills for hundreds of years. This can hurt animals and nature.
- Paper bags break down faster than plastic bags. But making them uses a lot of water and energy. This can cause trees to be cut down.
- Reusable bags are the best if you use them many times. Bags made from recycled materials are even better. If you use a reusable bag 10 to 150 times, you help the environment a lot.
- Always wash your reusable bags to keep them clean. This keeps your groceries safe too.
- Do not throw old bags away. Try to recycle or reuse them to make less trash.
- Pick a bag that works for your life. Keep it with you when you go shopping.
Measuring Environmental Impact
Life Cycle Analysis
When you want to know which shopping bag is better for the planet, you need to look at the whole story. This is where life cycle analysis comes in. You start by asking, “What is the purpose of this analysis?” Next, you gather data about every step, from making the bag to throwing it away. You look at how much energy, water, and raw materials each bag uses. You also check how much pollution and waste each bag creates. Finally, you study the results and think about ways to make better choices.
Here’s a simple table that shows the main steps in life cycle analysis:
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Goal and scope definition | You decide what you want to learn and which bags to compare. |
| Life cycle inventory | You collect facts about materials, energy, and waste for each bag. |
| Life cycle impact assessment | You measure things like pollution, global warming, and water use. |
| Interpretation | You look at the results and figure out how to help the environment. |
You see that each bag goes through many stages. These include getting raw materials, making the bag, moving it to stores, using it, and finally, disposing of it. The impact of each stage depends on the material. For example, plastic bags come from oil, paper bags come from trees, and cotton bags need a lot of water and energy.
Key Factors: Carbon, Water, Waste, Pollution
You might wonder what makes one bag better than another. You can look at four main things: carbon emissions, water use, waste, and pollution. These factors help you understand the environmental impact of each bag.
| Bag Type | Carbon Footprint | Water Consumption | Waste Generation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Bags | Lower | Less | Less |
| Paper Bags | Higher | More | More |
| Cotton Bags | Highest | Much More | More |
Plastic bags have a lower carbon footprint and use less water to make. However, they can cause a big environmental problem if you throw them away after one use. They do not break down easily and can harm wildlife. Paper bags need more water and energy to produce. They break down faster, but you must reuse them many times—sometimes up to 43 times—to make up for their impact. Cotton bags have the highest impact at first because they use a lot of water and energy. You need to use a cotton bag at least 131 times before it becomes better for the environment than a plastic bag.
Reusable bags made from non-woven polypropylene are a good choice if you use them at least 11 times. The more you reuse any bag, the less global warming and pollution you cause. You help the planet most when you pick a strong bag and use it again and again.
Tip: If you want to lower your environmental impact, choose a bag you can reuse many times. Try to avoid single-use plastic bags whenever possible.
You can see that life cycle analysis helps you make smart choices. It shows you that the best bag is the one you use the most. You can help fight global warming and reduce waste by thinking about how often you reuse your shopping bags.
Reusable Shopping Bags vs Plastic: Direct Comparison
When you look at reusable shopping bags vs plastic, you want to know which one is better for the planet. Let’s break it down step by step so you can see the real differences.
Production and Materials
You might think all bags are the same, but their materials and how they’re made make a big difference. Here’s a quick look at what goes into making each type:
| Bag Type | Raw Materials | Energy Use (megajoules) | Water Use (gallons) | Greenhouse Gas Emissions (tons of CO2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic | Natural gas, petroleum | 763 | 58 | 0.04 |
| Paper | Trees (14 million trees for 10 billion bags) | 2,622 | 1,004 | 0.08 |
| Cotton | Cotton (needs lots of water and chemicals) | N/A | N/A | N/A |
- Plastic bags come from oil and natural gas. They use less water and energy than paper or cotton bags.
- Paper bags need trees and lots of water. Making them uses more energy and creates more pollution.
- Cotton bags use a lot of water and chemicals to grow the cotton. They need the most resources at the start.
You can see that plastic bags use fewer resources to make, but that’s not the whole story.
Environmental Pros and Cons
Carbon and Water Use
Let’s talk about carbon and water. These are two big things that affect the environment.
- Plastic bags have a lower carbon footprint and use less water than paper or cotton bags.
- Paper bags use about 50 times more water than plastic bags. They also create more air pollution.
- Cotton bags need the most water and energy. You need to use a cotton bag thousands of times to make up for its production.
Waste and Pollution
Waste and pollution are big problems when you compare reusable shopping bags vs plastic.
| Bag Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Paper Bags | Biodegradable, can be made from recycled materials | Deforestation, chemical waste, less durable, not waterproof |
| Plastic Bags | Durable, waterproof, cheaper, easy to store | Environmental pollution, not biodegradable, adds to plastic waste |
| Reusable Bags | Lower environmental impact over time, can replace many single-use bags | Depends on material and how often you use them, may need more resources to make |
- Plastic bags can last a long time, but they don’t break down. They can end up in rivers and oceans, hurting animals.
- Paper bags break down faster, but making them can lead to cutting down trees and chemical waste.
- Reusable shopping bags can last for years. If you use them often, you create less waste. Some reusable bags, like those made from polypropylene, are hard to recycle, but their durability means you don’t need to throw them away often.
Note: If you use reusable shopping bags, remember to wash them. Studies show they can collect bacteria if you don’t clean them.
Reuse Thresholds
Here’s where things get interesting. The number of times you use a bag really matters. This is called the reuse threshold. It tells you how many times you need to use a bag before it becomes better for the environment than a single-use plastic bag.
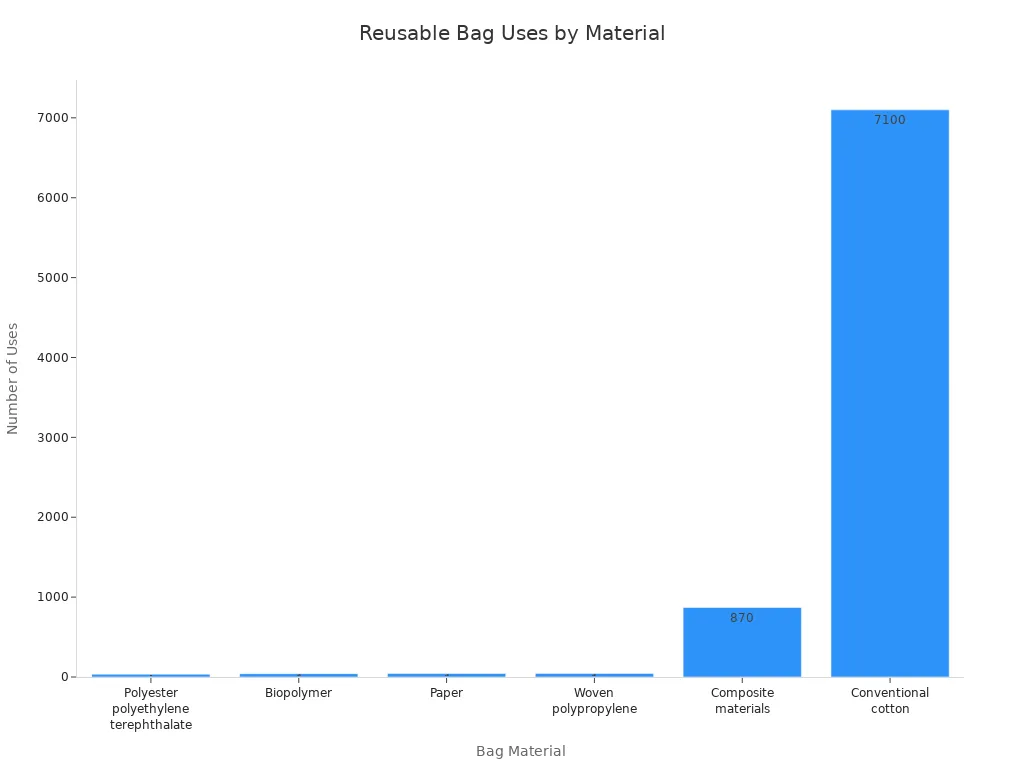
- Polypropylene bags need to be used about 45 times to have a lower environmental impact than plastic bags.
- Paper bags need to be reused five times to be better than plastic.
- Cotton bags need to be reused between 50 and 150 times, but some studies say up to 7,100 times, to match the impact of plastic bags.
- Cloth bags, like jute or canvas, need 30 to 50 uses to make a difference.
- Composite reusable bags can need hundreds of uses.
If you use your reusable shopping bags every week, you can easily reach these numbers. The more you use your bag, the better it is for the planet.
Tip: Choose a strong, reusable bag you like. Use it as often as you can. That’s the best way to lower your environmental impact.
So, when you compare reusable shopping bags vs plastic, you see that plastic bags use fewer resources at first, but they create more waste and pollution. Reusable shopping bags need more resources to make, but if you use them many times, they become the better choice for the environment.
Plastic Bags
How They’re Made
You might see plastic bags everywhere, but do you know how they’re made? The process starts with raw materials like natural gas or petroleum. These get refined to create polyethylene resins, such as LDPE and HDPE. Manufacturers melt these plastic pellets and push them through a machine to form a thin film. After cooling, workers cut and seal the film into the shape of bags. Sometimes, they add color or other features to make the bags stronger or more flexible.
Here’s a quick look at the steps:
- Raw material extraction from oil or natural gas.
- Creation of polyethylene resins.
- Film extrusion to make thin sheets.
- Cutting and sealing to shape the bags.
You end up with lightweight, waterproof plastic bags that are cheap and easy to produce.
Environmental Impact
Carbon Emissions
Plastic bags have a lower carbon footprint during production compared to paper or cotton bags. You use less energy and water to make them. However, the environmental impact doesn’t stop there. When you throw away single-use plastic bags, they don’t break down quickly. They can stay in landfills for hundreds of years. As they break apart, they release toxic substances into the soil and air. This pollution can harm your health and the planet.
Litter and Wildlife
Plastic bags often end up as litter. You might see them blowing down the street or stuck in trees. When they reach rivers and oceans, they become a big problem for marine life. Fish, turtles, and birds can mistake plastic bags for food. If they eat them, they can choke or starve. Marine animals can also get tangled in plastic, which can injure or kill them. Plastic bags block storm drains and cause flooding in cities. They even damage farmland by polluting the soil and water.
Did you know? Plastic bags are one of the top items found during beach cleanups. They threaten marine ecosystems and tourism.
Reuse and Disposal
You can reuse plastic bags in many ways. Some people use them to line trash cans, store items, or make crafts. Communities sometimes upcycle plastic bags into sleeping mats for people in need. If you want to reduce waste, you can choose reusable shopping bags instead of plastic. Many stores give you a discount when you bring your own bag.
When you recycle plastic bags, workers collect and sort them. They clean the bags, shred them into flakes, and melt them down to make new products. Advanced recycling methods can even turn plastic waste into energy. Still, recycling rates for plastic bags remain low. Most end up in landfills or as litter, causing long-term problems for the environment and marine life.
Tip: Try to reuse plastic bags as much as possible. Switch to reusable bags to help protect marine animals and reduce pollution.
Paper Bags
Production Process
You might see paper bags at the grocery store or when you buy takeout. Have you ever wondered how they’re made? The process starts with materials like kraft paper, test-liner paper, and whitetop paper. Workers shred and pulp the paper, then clean it to remove dirt and ink. Next, machines print designs, cut the paper into shapes, fold it, and glue the edges to make strong bags. The process uses more steps than plastic bag manufacturing, which usually just melts plastic pellets and molds them into shape.
Here’s a table that shows how making paper bags compares to plastic bags:
| Step | Paper Bag Production | Plastic Bag Production |
|---|---|---|
| Material Sourcing | Kraft, test-liner, whitetop paper | Petroleum-based materials |
| Preparation | Shredding, pulping, cleaning | Fewer steps, more streamlined |
| Manufacturing | Printing, cutting, folding, gluing | Extrusion and molding |
| Environmental Impact | More sustainable materials | Fewer carbon emissions per unit |
You can see that paper bags use eco-friendly materials, but the process takes more energy and water.
Environmental Impact
Water and Energy Use
When you look at the environmental impact of paper bags, you notice they need a lot of water and energy. Making paper bags uses more energy than making plastic bags. The machines that pulp, print, and glue the paper run for hours and use lots of electricity. Water helps clean and process the paper, but it adds up quickly. If you use a paper bag only once, the impact is even bigger.
Did you know? Paper bags can use up to 50 times more water than plastic bags during production.
Waste and Recycling
Paper bags break down faster than plastic bags, but they still create waste. If you throw them away, they can end up in landfills. When paper bags rot in landfills, they release greenhouse gases. You might think recycling solves the problem, but not all paper bags get recycled. Some have coatings or inks that make recycling harder. If you recycle your paper bags, you help save energy and reduce waste. Recycling paper bags also keeps them out of landfills and gives them a second life as new products.
Here are some ways you can help:
- Put clean paper bags in your recycling bin.
- Remove any food or grease before recycling.
- Choose bags made from recycled paper when you shop.
- Encourage your friends to recycle their paper bags too.
Reuse and End-of-Life
You can reuse paper bags for many things. Try using them to carry books, wrap gifts, or store items at home. If you reuse a paper bag several times, you lower its impact on the environment. When the bag wears out, recycling is the best option. If you compost paper bags, they break down and return to the soil. You help the planet most when you reuse and recycle your paper bags instead of throwing them away.
Tip: Always check if your local recycling program accepts paper bags. Some places have special rules for coated or colored bags.
Paper bags offer a greener choice than plastic if you use them more than once and recycle them. You make a difference every time you choose to reuse and recycle.
Reusable Bags
Types: Cotton, Polypropylene, Polyester
When you go shopping, you see many reusable bags. Each bag is made from a different material. Each material affects the environment in its own way. Here’s a table that shows the most common types:
| Type of Bag | Material Used | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Canvas | Organic Cotton | Biodegradable, decomposes without harmful residues. |
| Cotton | Organic and Regular | Organic has a lower environmental footprint. |
| Jute and Hemp | Jute and Hemp | Low environmental footprints, fewer chemicals and water. |
| Polypropylene | Polypropylene | Energy-intensive production, involves harmful chemicals. |
| Recycled PET | Recycled PET | Saves on new plastic production but energy-intensive. |
| Nylon | Nylon | Energy-intensive and polluting manufacturing process. |
You probably see cotton, polypropylene, and polyester bags the most. Cotton bags feel soft and strong. Polypropylene bags are shiny and waterproof. Polyester bags can be made from old plastic bottles. This helps reduce waste.
Production Impact
You might wonder how making these bags affects the earth. The answer depends on what the bag is made from. Here’s what happens when they are made:
- Cotton farming uses a lot of water and land. It also needs pesticides. This can hurt animals and plants.
- Polypropylene bags are made from plastic. They use less energy than cotton bags. But making them still uses chemicals and fossil fuels.
- Polyester bags come from crude oil. They make more greenhouse gases. If you pick recycled polyester, you help save resources.
Nonwoven polypropylene bags are tough and waterproof. If you use them many times, they have a lower carbon impact. Cotton bags need more resources at first. Organic cotton is better for the earth than regular cotton.
Tip: To help the planet, choose bags made from recycled or organic materials.
Environmental Benefits
Reusable bags are better than single-use plastic or paper bags. You help the earth every time you use one.
Durability and Reuse
Reusable bags last a long time. You can carry heavy things without the bag breaking. They hold more than thin plastic bags. You save money because you do not need to buy new bags often.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost-effective | You use reusable bags for years, so you buy fewer new bags. |
| Strong | These bags carry more weight and rarely tear. |
| Reliable and durable | You can trust reusable bags to hold your items safely. |
Waste Reduction
When you use reusable bags, you help make less waste. You save oil, water, and trees. You also keep plastic bags out of landfills and oceans. This helps protect animals and keeps your town cleaner.
- You use fewer single-use bags.
- You keep plastic out of nature.
- You help save energy and materials.
Note: Every time you reuse your bag, you help the earth. Small actions can make a big difference!
How Many Uses Needed
You may wonder how many times you must use reusable bags to help the earth. The answer depends on what your bag is made of. Some bags need only a few uses to help. Others need many more trips to the store.
Here is a table that shows how many times you should use each type of reusable bag to make up for making them, compared to single-use bags:
| Material Type | Approx. Uses to Reach Break-Even |
|---|---|
| Non-Woven Polypropylene (NWPP) | ~10–30 uses |
| rPET (Recycled Polyester) | ~20–40 uses |
| Organic Cotton | ~75–150 uses |
| Canvas (Heavy Cotton) | 100+ uses (varies by weight) |
| Jute | ~35–75 uses |
Non-woven polypropylene bags need the least uses. If you use one for a month or two, you already help the earth. Recycled polyester bags need a few more uses, but you still reach the break-even point fast. Cotton and canvas bags need many more uses. If you use a cotton bag every week, you may need to use it for two years before it is better than a plastic bag.
Here is a chart that shows the lowest and highest number of uses needed for each reusable bag material:
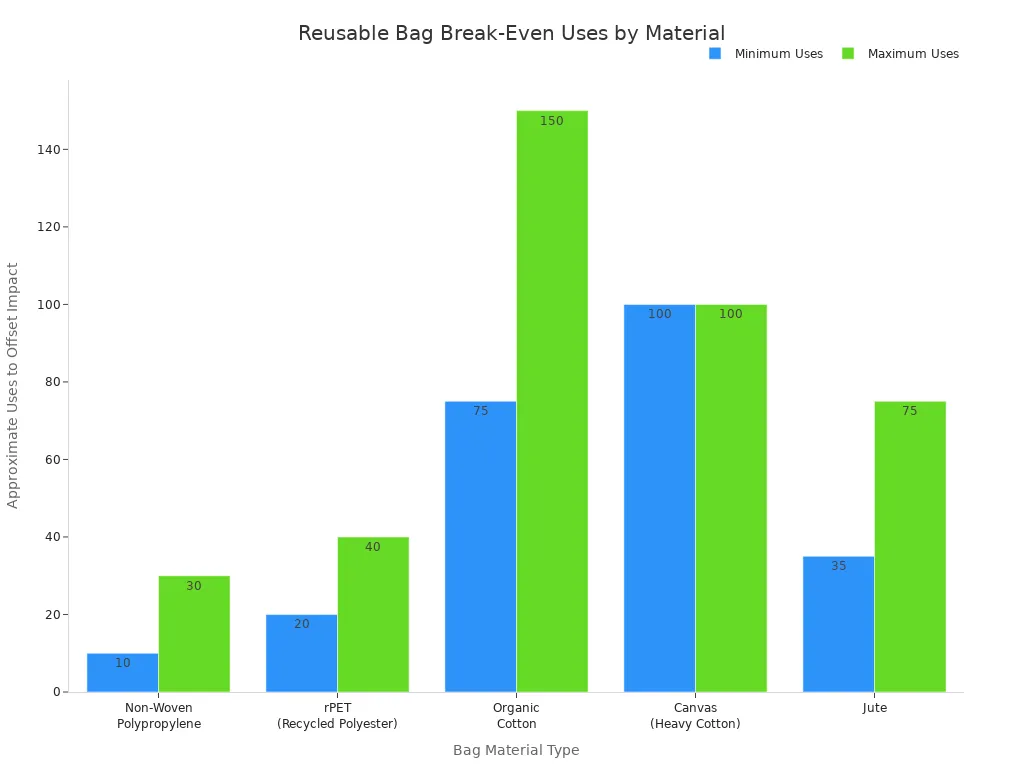
You may ask, “Why do cotton bags need so many uses?” Cotton farming uses a lot of water and energy. The more you use your cotton bag, the more you spread out its impact. Polypropylene and recycled polyester bags use less water and energy. This means you reach the break-even point faster.
Here are some quick facts to remember:
- Cotton bags need about 75–150 uses to make up for their impact.
- Non-woven polypropylene bags need about 10–30 uses.
- Recycled polyester bags need around 20–40 uses.
- Canvas bags need over 100 uses.
If you want your reusable bags to matter, use them as much as you can. Try to keep some in your car or near your front door. Make it a habit to bring them when you shop. The more you use your bags, the more you help cut down waste and pollution.
Tip: Pick reusable bags that work for you. If you shop a lot, a strong polypropylene or recycled polyester bag may be best. If you like cotton or canvas, plan to use them for many years.
You make a big difference when you use your bags again and again. Every trip to the store helps. You protect the earth, save resources, and keep your town cleaner.
Summary Table: Bag Comparison
Environmental Metrics
You want to see how each bag stacks up. Here’s a table that shows the main environmental facts about plastic, paper, and reusable bags. This makes it easy for you to compare and decide which bag fits your needs.
| Type of Bag | Environmental Impact | Key Data |
|---|---|---|
| Plastic Bags | Stay in the environment for hundreds of years. | Takes 500 to 1,000 years to break down in landfills. |
| Add to marine pollution and harm wildlife. | Millions of metric tons of plastic enter oceans every year. | |
| Use up fossil fuels during production. | Needs about 12 million barrels of oil each year. | |
| Paper Bags | Need lots of water and energy to make. | Uses four times more energy to produce than plastic bags. |
| Cause deforestation and loss of animal habitats. | 42% of global industrial wood harvest goes to paper production. | |
| Do not last long and get thrown away quickly. | Shorter lifespan than reusable bags. | |
| Reusable Bags | Cotton bags last a long time and can be used many times. | Cotton bags have a longer lifespan than single-use bags. |
| Upcycled bags help keep waste out of landfills. | Upcycling cuts down on textile waste. | |
| Bags made from recycled materials save energy. | Using recycled materials lowers the carbon footprint. |
You can see that plastic bags stick around for centuries and pollute oceans. Paper bags use more resources and lead to deforestation. Reusable bags, especially those made from recycled or upcycled materials, help you cut down on waste and save energy.
Key Takeaways
You might still wonder which bag is best for the environment. Here are the main points you should remember:
- Plastic bags are cheap and easy to use, but they last forever in landfills and oceans. They harm animals and use up oil.
- Paper bags break down faster, but they need a lot of water and energy to make. They also lead to cutting down trees.
- Reusable bags help the most if you use them many times. Cotton and upcycled bags last longer and keep waste out of landfills. Bags made from recycled materials save energy and lower pollution.
Tip: You make the biggest difference when you pick a strong reusable bag and use it every time you shop. Try to avoid single-use bags whenever you can.
Here’s a quick list to help you choose:
- Pick a reusable bag you like and will use often.
- Wash your bag to keep it clean and safe.
- Recycle or upcycle old bags when they wear out.
- Remember, every time you reuse a bag, you help the planet.
You have the power to make a smart choice. When you use your bag again and again, you protect nature, save resources, and keep your community clean.
Tips to Reduce Your Impact
You want to make a difference for the planet every time you shop. Here are some easy ways to lower your environmental impact and get the most out of your shopping bags.
Choosing the Right Bag
Picking the best bag depends on how you plan to use it. You should think about more than just the look or price. Here’s a table to help you compare what matters most:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Production Impact | How much energy, water, and resources go into making the bag. |
| Reuse Potential | How many times you can use the bag before it wears out. |
| Disposal Methods | What happens to the bag when you throw it away—can you recycle or compost it? |
| Carbon Footprint | How much carbon is released during the bag’s life, from making it to disposal. |
| Resource Consumption | How much water and energy are used to make plastic, paper, or reusable bags. |
If you shop often, a strong reusable bag is a smart choice. If you forget your bag sometimes, you might want a few paper bags as backup. Try to avoid plastic bags when you can, since they stick around for a long time and can harm wildlife.
Tip: Choose a bag that fits your lifestyle. The best bag is the one you will use again and again.
Maximizing Reuse
You can help the earth most by using your bags as many times as possible. Here are some simple ways to get the most out of every bag:
- Keep reusable bags in your car or by the door so you never forget them.
- Wash your bags regularly to keep them clean and safe.
- Upcycle old bags into cleaning rags or storage pouches instead of throwing them away.
- Donate bags in good shape to local charities or friends.
- Teach your family and friends about the benefits of reusing bags.
- Try making crafts or unique items from old bags to give them a new life.
When you reuse bags, you cut down on waste and save resources. You also help reduce the need for new plastic bags, which means less pollution in rivers and oceans.
Note: Every time you reuse a bag, you help keep plastic out of nature and protect animals.
Proper Disposal
When your bags wear out, you still have choices that help the planet. Here’s what you can do:
- Check if your bag can go in the recycling process. Some bags, like plastic bags, need special drop-off spots at grocery stores.
- Use bags until they are worn out. This gives you the most value and lowers your impact.
- Upcycle or donate bags that are still in good shape.
- Take reusable bags to local recycling centers or textile recycling programs.
- Join community collection events or use online recycling directories to find the right place for your bags.
- For plastic bags, never put them in your curbside bin. They can clog machines at recycling centers. Drop them off at stores with plastic film recycling programs.
Paper bags can go in your home recycling bin if they are clean and dry. Reusable bags made from fabric or polypropylene may need to go to a special recycling center. Always check local rules before tossing any bag.
Tip: Proper disposal keeps bags out of landfills and helps turn old materials into something new.
You have the power to make a big difference. By choosing the right bag, reusing it often, and disposing of it the right way, you help create a cleaner, greener world.
Conclusion
You help the environment most when you reuse your bags many times. This makes up for the resources used to make them. Many people use plastic bags as trash can liners. But most plastic bags still end up in landfills. Using reusable bags again and again is better for the earth. It helps lower waste and supports a greener world. If you want a special bag, we have many reusable shopping bags to pick from. Our OEM and ODM services can help your business go green. Reach out to us to design your own eco-friendly bag!
FAQ
How many times should you use a reusable bag?
You should use your reusable bag at least 10 to 150 times, depending on the material. Polypropylene bags need fewer uses. Cotton bags need more. The more you use your bag, the better for the environment.
Can you recycle plastic shopping bags?
You can recycle plastic bags at special drop-off bins in many grocery stores. Never put them in your curbside bin. They can jam recycling machines. Always check your local recycling rules.
Are paper bags better than plastic bags?
Paper bags break down faster than plastic bags. They use more water and energy to make. If you reuse and recycle paper bags, you help the planet more than using single-use plastic bags.
What is the best material for a reusable shopping bag?
Polypropylene and recycled polyester bags offer a good balance. They last long and need fewer uses to offset their impact. Cotton bags feel nice but need many uses to be eco-friendly.
How do you clean reusable shopping bags?
You can wash most reusable bags in cold water with mild soap. Let them air dry. Clean your bags often to keep them safe and fresh. Always check the care label before washing.
Do reusable bags carry germs?
Reusable bags can collect germs if you don’t clean them. Wash your bags regularly. Keep raw foods separate from other items. This helps keep your groceries and family safe.
What should you do with old reusable bags?
You can donate, recycle, or upcycle old bags. Some textile recycling centers accept fabric bags. You can turn worn-out bags into cleaning cloths or storage containers. Get creative and give your bags a second life!




